You are now leaving the ISTURISA (osilodrostat) website. This link will take you to a site maintained by a third party who is solely responsible for its content.
Signs & Symptoms
Is it Cushing’s disease?
Knowing what to look for is important when evaluating the clinical presentation of hypercortisolism, which can present with varying phenotypes.1 Clinical suspicion of Cushing’s disease may arise without a complete picture of classic discriminatory symptoms, especially if other comorbidities are present.2,3
Select a highlighted area below, or tap the arrows to review CD symptoms:
 Classic Discriminatory Symptom
Classic Discriminatory Symptom
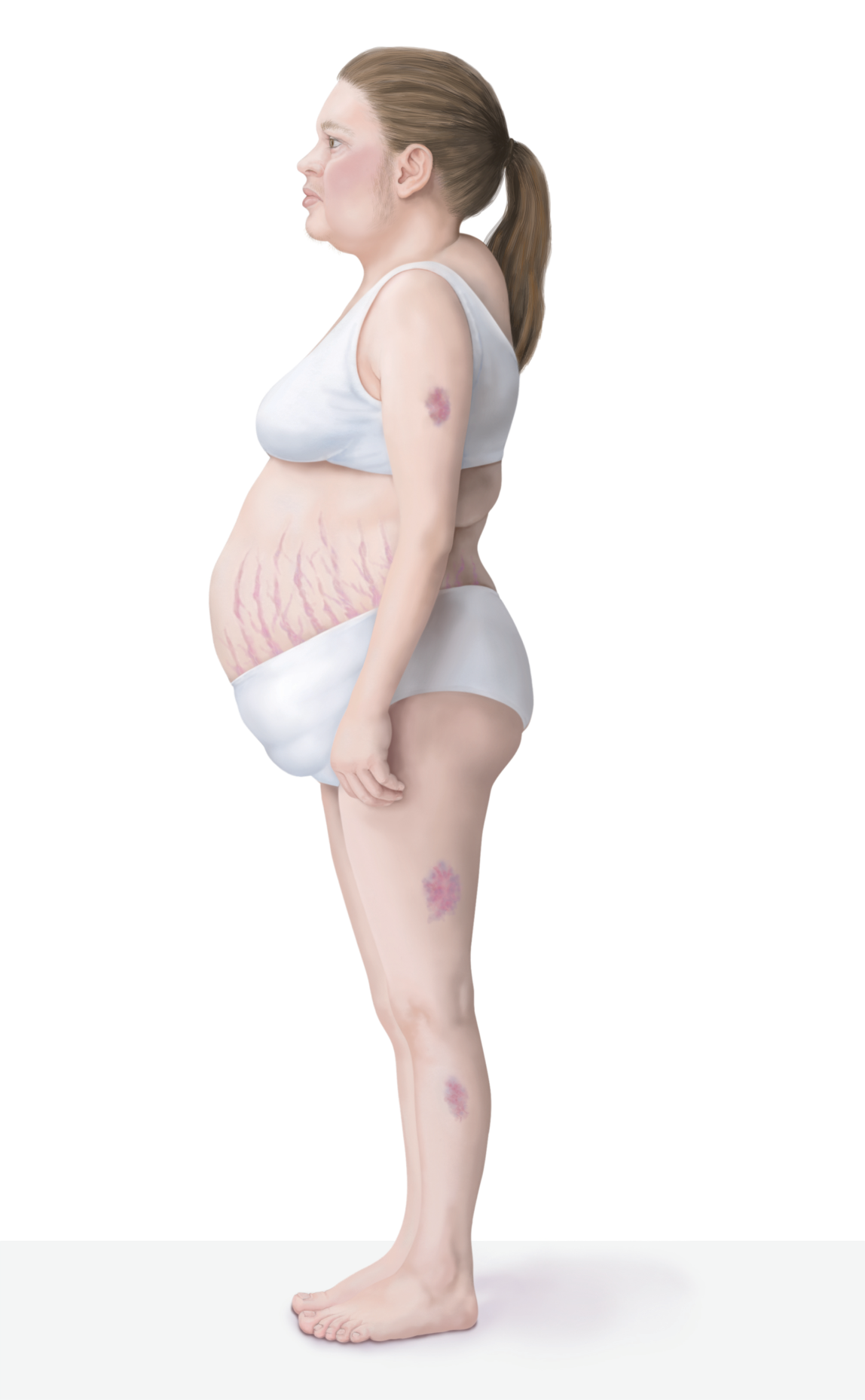
 Plethora3
Plethora3
 Purpura with no obvious trauma3
Purpura with no obvious trauma3
 Reddish-purple striae2,3
Reddish-purple striae2,3
 Proximal muscle weakness2,3
Proximal muscle weakness2,3
Clinical Features
The signs and symptoms of CD can be confusing:1,6
- Signs and symptoms vary from patient to patient
- Not all signs and symptoms are obvious, especially early in the progression
- Milder hypercortisolism may not present classically; it may present as a constellation of subtle or inexplicable signs and symptoms
Cushing’s Disease: Disease State Overview
Understand the impact of hypercortisolism, as well as screening and diagnosis.
Watch video on-demandINDICATIONS AND USAGE
ISTURISA (osilodrostat) is a cortisol synthesis inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adult patients with Cushing’s disease for whom pituitary surgery is not an option or has not been curative.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Warnings and Precautions
-
Hypocortisolism: ISTURISA lowers cortisol levels and can lead to hypocortisolism and sometimes life-threatening adrenal insufficiency. Lowering of cortisol can cause nausea, vomiting, fatigue, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, and dizziness. Significant lowering of serum cortisol may result in hypotension, abnormal electrolyte levels, and hypoglycemia.
Hypocortisolism can occur at any time during ISTURISA treatment. Evaluate patients for precipitating causes of hypocortisolism (infection, physical stress, etc). Monitor 24-hr urine free cortisol, serum or plasma cortisol, and patient’s signs and symptoms periodically during ISTURISA treatment.
Decrease or temporarily discontinue ISTURISA if urine free cortisol levels fall below the target range, there is a rapid decrease in cortisol levels, and/or patients report symptoms of hypocortisolism. Stop ISTURISA and administer exogenous glucocorticoid replacement therapy if serum or plasma cortisol levels are below target range and patients have symptoms of adrenal insufficiency. After ISTURISA discontinuation, cortisol suppression may persist beyond the 4-hour half-life of ISTURISA. Please see section 5.1 of full Prescribing Information.
Educate patients on the symptoms associated with hypocortisolism and advise them to contact a healthcare provider if they occur.
- QTc Prolongation: ISTURISA is associated with a dose-dependent QT interval prolongation which may cause cardiac arrhythmias. Perform an ECG to obtain a baseline QTc interval measurement prior to initiating therapy with ISTURISA and monitor for an effect on the QTc interval thereafter. Correct hypokalemia and/or hypomagnesemia prior to ISTURISA initiation and monitor periodically during treatment with ISTURISA. Use with caution in patients with risk factors for QT prolongation and consider more frequent ECG monitoring. Please see section 5.2 of full Prescribing Information.
- Elevations in Adrenal Hormone Precursors and Androgens: ISTURISA blocks cortisol synthesis and may increase circulating levels of cortisol and aldosterone precursors and androgens. This may activate mineralocorticoid receptors and cause hypokalemia, edema and hypertension. Hypokalemia should be corrected prior to initiating ISTURISA. Monitor patients treated with ISTURISA for hypokalemia, worsening of hypertension and edema. Inform patients of the symptoms associated with hyperandrogenism and advise them to contact a healthcare provider if they occur. Please see section 5.3 of full Prescribing Information.
Adverse Reactions
- Most common adverse reactions (incidence >20%) are adrenal insufficiency, fatigue, nausea, headache, and edema.
- To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Recordati Rare Diseases Inc. at 1-888-575-8344, or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- CYP3A4 Inhibitor: Reduce the dose of ISTURISA by half with concomitant use of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor.
- CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 Inducers: An increase of ISTURISA dosage may be needed if ISTURISA is used concomitantly with strong CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 inducers. A reduction in ISTURISA dosage may be needed if strong CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 inducers are discontinued while using ISTURISA.
Use in Specific Populations
- Lactation: Breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with ISTURISA and for at least one week after treatment.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ISTURISA (osilodrostat) is a cortisol synthesis inhibitor indicated for the treatment of adult patients with Cushing’s disease for whom pituitary surgery is not an option or has not been curative.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Warnings and Precautions
-
Hypocortisolism: ISTURISA lowers cortisol levels and can lead to hypocortisolism and sometimes life-threatening adrenal insufficiency. Lowering of cortisol can cause nausea, vomiting, fatigue, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, and dizziness. Significant lowering of serum cortisol may result in hypotension, abnormal electrolyte levels, and hypoglycemia.
Hypocortisolism can occur at any time during ISTURISA treatment. Evaluate patients for precipitating causes of hypocortisolism (infection, physical stress, etc). Monitor 24-hr urine free cortisol, serum or plasma cortisol, and patient’s signs and symptoms periodically during ISTURISA treatment.
Decrease or temporarily discontinue ISTURISA if urine free cortisol levels fall below the target range, there is a rapid decrease in cortisol levels, and/or patients report symptoms of hypocortisolism. Stop ISTURISA and administer exogenous glucocorticoid replacement therapy if serum or plasma cortisol levels are below target range and patients have symptoms of adrenal insufficiency. After ISTURISA discontinuation, cortisol suppression may persist beyond the 4-hour half-life of ISTURISA. Please see section 5.1 of full Prescribing Information.
Educate patients on the symptoms associated with hypocortisolism and advise them to contact a healthcare provider if they occur.
- QTc Prolongation: ISTURISA is associated with a dose-dependent QT interval prolongation which may cause cardiac arrhythmias. Perform an ECG to obtain a baseline QTc interval measurement prior to initiating therapy with ISTURISA and monitor for an effect on the QTc interval thereafter. Correct hypokalemia and/or hypomagnesemia prior to ISTURISA initiation and monitor periodically during treatment with ISTURISA. Use with caution in patients with risk factors for QT prolongation and consider more frequent ECG monitoring. Please see section 5.2 of full Prescribing Information.
- Elevations in Adrenal Hormone Precursors and Androgens: ISTURISA blocks cortisol synthesis and may increase circulating levels of cortisol and aldosterone precursors and androgens. This may activate mineralocorticoid receptors and cause hypokalemia, edema and hypertension. Hypokalemia should be corrected prior to initiating ISTURISA. Monitor patients treated with ISTURISA for hypokalemia, worsening of hypertension and edema. Inform patients of the symptoms associated with hyperandrogenism and advise them to contact a healthcare provider if they occur. Please see section 5.3 of full Prescribing Information.
Adverse Reactions
- Most common adverse reactions (incidence >20%) are adrenal insufficiency, fatigue, nausea, headache, and edema.
- To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Recordati Rare Diseases Inc. at 1‑888‑575‑8344, or FDA at 1‑800‑FDA‑1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions
- CYP3A4 Inhibitor: Reduce the dose of ISTURISA by half with concomitant use of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor.
- CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 Inducers: An increase of ISTURISA dosage may be needed if ISTURISA is used concomitantly with strong CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 inducers. A reduction in ISTURISA dosage may be needed if strong CYP3A4 and CYP2B6 inducers are discontinued while using ISTURISA.
Use in Specific Populations
- Lactation: Breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with ISTURISA and for at least one week after treatment.
